 Before we barge into adopting cloud solution to optimize our resources and reduce TCO, lets us understand the problem statement here. In IT landscape Cloud is clearly an enthralling and rewarding solution. Its scalability, availability, flexibility, customized or “Pay-as-u-Go” and many more features helps improve efficiency and also productivity. There are vendors coming up with good solutions and offerings customizing one’s requirement ranging from compute, storage, network, servers, and applications, up time, BCP, DR and what not!!! However, some time approach to choose cloud solution amongst Private, Public, hybrid etc. becomes confusing while making a trade-off between security and cost and subsequently overall solution gets complex, bigger and complicated.
Before we barge into adopting cloud solution to optimize our resources and reduce TCO, lets us understand the problem statement here. In IT landscape Cloud is clearly an enthralling and rewarding solution. Its scalability, availability, flexibility, customized or “Pay-as-u-Go” and many more features helps improve efficiency and also productivity. There are vendors coming up with good solutions and offerings customizing one’s requirement ranging from compute, storage, network, servers, and applications, up time, BCP, DR and what not!!! However, some time approach to choose cloud solution amongst Private, Public, hybrid etc. becomes confusing while making a trade-off between security and cost and subsequently overall solution gets complex, bigger and complicated.
A private cloud could be built using our own resources in our data center while keeping control as well as to shoulder the management overhead, whereas, Public cloud services us of that management burden but at the expense of some control. Hybrid solution approach might make it possible to realize the best of both worlds, but we still have to start from either private or public as the base for operations.
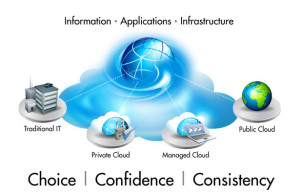
Let’s take a dip inside overall solution framework with respect to what it is, how it works, pros and cons in different cloud solution categories and then evaluate the one that will stand better for particular type of business from others.
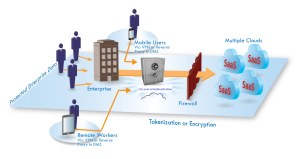
Cloud components and migration: As most of us know that cloud solution comprises of at least three components such as IaaS (Infrastructure As a Service), SaaS(Software as a Service) and PaaS(Platform as a service). As names implies, IaaS components takes care of provisioning server, storages, Compute, n/w part etc. It primarily uses virtualization techniques following either Type 1 or Type 2. Type 1 is to set up machine directly with hypervisors such as VMware ESX/ESXi while having management software deployed elsewhere such as vCenter. Type 2 is installing and setting up virtualization on OS such as VMware Fusion, virtual box etc. PaaS is to give platform or framework to the developers for application development that includes design, coding, testing etc. As an analogy, PaaS enables developers to develop application using software components similar to a technician uses macro components to automate certain activities in an Excel sheet. SaaS component is one of the fastest growing cloud application services. Google applications, Salesforce, Cisco Webex etc. are some of the most used applications. The delivery model is primarily web channels, no need for installations. At most you might have to use plugins in some areas.
Some of the key determinants in choosing cloud solution type are security and compliance, the ease of migration from traditional data center to the cloud, range of services available (DR, Agility of application induction etc.), cost, performance, tenants etc . If you’re using SaaS or other cloud applications, you should ensure that any link used to connect or upload information into your infrastructure is secured through SSL or similar protocols. There are also encryption gateway products that encrypt data before it leaves the data center and migrates to SaaS environments such as Salesforce.
Most IaaS run on virtualized servers, as they are far easier to spin up and decommission than physical hardware. Plus, service providers have far better control for load balancing and scalability. Private cloud may have bit of less flexibility in giving high and continuous throughput since load balancing resources may not be many. Due to organizational policy and data confidentiality requirement business would not want to go into Public Cloud but Private Cloud, so is business comfortable with probably less span of load balancing and thereby not having great throughput?
Where to start with: Question remains where to start with, private or public? Business doesn’t want to be left behind in the race of cloud migration to harness benefits coming from the solution. But it wouldn’t compromise on security; there could also be inherent inertia to the change and migration.In the beginning safest moment looks to move to the private cloud and experience the effect.
Private cloud lives within our firewall and organizations that deal in private and proprietary data (for example financial services, healthcare, and government institutions) simply cannot risk third-party access to sensitive data, and even face legal ramifications for breaches. Private cloud offer a way for these organizations to transition their existing data center investments into a more scalable, user-friendly model while maintaining control over private data.
Organizations have made huge investment in setting up traditional DC including servers, storages, various infrastructure components, labor cost and many more. Transformation to Private cloud makes sense to get best out of the investment and features that cloud offers without compromising too much.
With an enterprise private cloud, administrators receive at least two major benefits, (a) dramatic increase in the utilization of existing infrastructure, which drives down costs and limits the need for future purchases. With cloud-based capacity management, administrators can increase utilization from around 40% (with virtualization alone) up to 75% to 85%, besides they will have control and detailed insight into exactly how that infrastructure is being used. (b) Secondly, automation engine enable administrators to do more in less time while putting focus on strategic functions, such as IT service design and policy management.
Private cloud gives space to experiment features, test and tweak configuration and attributes in the evolving stage while migrating IT set up from traditional data center to the cloud.
In the public cloud, vendor lock-in is a reality, and we are at the mercy of the providers and their choices about technology, vendors, policy and standards.
Public cloud set up involves multiple players in fixing problems if something goes wrong. Multiple players such as Storage, n/w guys, external vendors, multiple processes etc. all put together creates confusion while consuming time to fix things quickly.
Public cloud solution has its own merit and probably the best way forward for small player and fledging industries. In most scenarios, I have found security requirement for SMEs are minimal in the beginning while giving space for “What-if” scenario to tweak and calibrate approach. SME can gradually add on public cloud features including SSL, OpenSSL security features. Public cloud pay-as-u-Go model suits the best to SME while simultaneously testing all cloud features and promises as time passes by.
Small business with short term to long term plan preferably partner with vendors like AWS/EC2, MS/Azure, Saleforce etc. to experiment different approaches and evaluate which one would be best for their business. For example, let’s say, I want to set up a new e-commerce business in providing payment service. I might start by designing a small cloud payment solution for small set of consumers near my neighborhood rather than going with a full blown solution for whole segment of consumers ranging from grocery store to consumer durables to stationary items etc. I would prefer to host everything in the public cloud and leverage the shared resources while having to pay only my storage and CPU requirement. There could be some spike in the consumer demand at times so be it. I don’t have to worry about anything except focusing how to grow my customer base.
Public cloud generally comes with the blurriness about quality of security concerning to the related business nature & set up. While security is a challenge, there are ways to meet compliance rules and mitigate risk. Generally Public cloud solutions are built with the framework having characteristics of multi-tenancy, obscuring data from others, data tagging, firewall etc. that should be enough to trust security.
However, I haven’t heard of any security problem in public cloud or any data threat from its infrastructure or underlying process. On the contrary, tons of data breach have been reported from corporate data center either traditional or private cloud, Please visit my last blog to get some of the examples @ http://www.techmanthan.com/index.php/2015/07/19/it-security-race-between-it-evolution-and-security-threat/
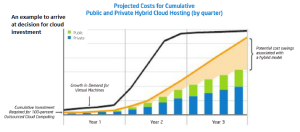
Bigger picture: Any IT solution to support business need to have short term to long term strategy. Cloud Investments are to be made factoring growth forecast, RISK appetite, ability to carry out phase wise approach (e.g Let’s start with public while keeping confidential or policy related application in house or may be hybrid approach) and many more. We need to have provisions to access applications anytime from anywhere whether applications are legacy or modern type. Application development process with the ability to share code (GitHub type solution), share data, collaborative method to test and fix bugs with increase the throughput and reduce time to market. Recently NASA migrated 65 legacy applications to AWS private cloud while looking at doing the same for rest of intranet, internet, data intensive applications exceeding 1500 applications in coming days. The agency also has 10 “sensitive” applications—such as its engineering network, which has 3.5 million to 5 million documents for engineers across NASA—on Amazon’s GovCloud (Private Cloud), an isolated section of the AWS cloud for government agencies with specific regulatory and compliance requirements. This migration itself curtailed the cost of operation by 40% barring further cleaning and optimization on the card.
While public cloud services are proving their worth and attracting new converts every day, we will ultimately see the emergence of a hybrid public/private mix that can satisfy any lingering security or regulatory concerns about particular data. But without compromising their most sensitive data, businesses will move as much of their workloads as possible to take advantage of the flexibility and agility offered by public cloud services.
In the summary, Private cloud seems to be clear choice for big enterprises and governmental agencies looking to reap benefit of cloud computing without losing control of data and compromising security policy. Whereas fledgling Industry, SMEs, Industries with strong projection of exponential data growth etc. should be leaning towards public cloud. Short term to long term strategy should define the road map from Private to hybrid to the public cloud. My attempt is to make IT establishment and business aware of such certain critical determining factors must come in play before jumping into cloud race and avoid surprises, cost overrun etc. at later stage.